Which Soil is Suitable for Tea Cultivation?
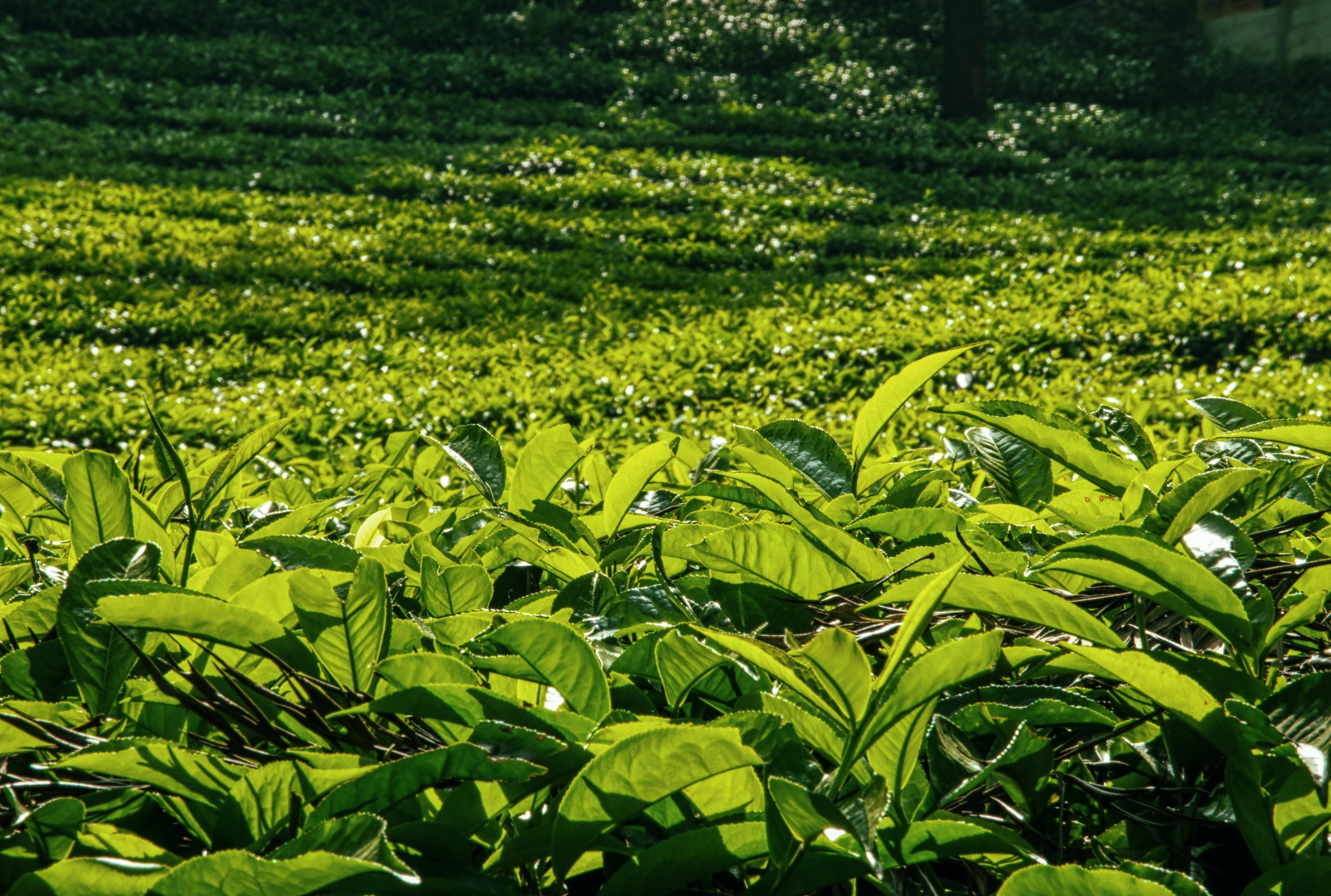
Tea is one of the most popular beverages in the world, and the cultivation of tea requires specific soil conditions to ensure high-quality tea production. Soil quality plays a critical role in tea cultivation, affecting the growth, yield, and quality of tea plants. Different types of soil have unique properties that affect tea growth and flavor, so it is essential to choose the right soil for tea cultivation.
The ideal soil for tea cultivation is well-drained, slightly acidic, and rich in organic matter. The soil should also be fertile and have good water-holding capacity. Tea plants require a consistent supply of water, and poorly drained soil can lead to root rot and other diseases. Soil with high organic matter content provides nutrients to tea plants, which promote healthy growth and development.
Soil pH
In general, tea grows best in soils with a pH range of 5.0 to 6.5. Soil with a pH lower than 5.0 can be too acidic for tea plants, while soil with a pH higher than 6.5 can be too alkaline. The pH level of the soil can be adjusted by adding lime or sulfur to the soil, depending on the pH level.
Tea cultivation is a complex and delicate process that requires careful attention to a number of factors, including soil pH. Soil pH is the measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, which can have a significant impact on the growth and health of tea plants. In this article, we will explore the importance of soil pH in tea cultivation and how it affects the quality and flavor of the tea.
The optimal soil pH for tea cultivation varies depending on the type of tea being grown, but in general, a pH range of 4.5 to 5.5 is considered ideal. This is because tea plants thrive in slightly acidic soil, which allows them to absorb nutrients more easily. If the soil pH is too high or too low, it can result in nutrient deficiencies, which can stunt growth and reduce the yield of the tea plants.
One of the key nutrients that is affected by soil pH is aluminum. In acidic soils, aluminum can become more soluble, which can be toxic to tea plants. This can result in stunted growth and reduced yield, as well as poor flavor and quality of the tea. On the other hand, in alkaline soils, aluminum becomes less soluble, which can lead to aluminum deficiencies in the tea plants.
In addition to aluminum, soil pH also affects the availability of other essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are crucial for the growth and development of tea plants, and if they are not available in the right amounts, it can have a negative impact on the quality and flavor of the tea.
Soil pH can also affect the microbial activity in the soil. Certain bacteria and fungi thrive in acidic soils, while others prefer alkaline conditions. The microorganisms in the soil play a critical role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients, so it is important to maintain a balance of microorganisms that are beneficial for tea cultivation.
To maintain the optimal soil pH for tea cultivation, it is important to monitor the pH levels regularly and make any necessary adjustments. This can be done by adding lime to raise the pH of acidic soils or adding sulfur to lower the pH of alkaline soils. It is also important to maintain good soil structure and fertility by adding organic matter, such as compost or manure.
Soil Texture
Soil texture refers to the physical composition of soil, including the size and distribution of particles such as sand, silt, and clay. These particles determine the soil’s structure and porosity, which in turn affects the soil’s ability to hold water, nutrients, and air. In tea cultivation, the ideal soil texture depends on a variety of factors, including the climate, altitude, and rainfall of the region.
One of the most important factors affecting soil texture in tea cultivation is drainage. Tea plants require well-drained soil to grow and thrive, as waterlogged soil can lead to root rot and other diseases. Sandy soils are known for their excellent drainage, making them a popular choice for tea cultivation in regions with high rainfall. However, sandy soils are also prone to erosion and can lack nutrients, which can affect the quality of the tea.
Silt and clay soils, on the other hand, tend to hold more water and nutrients, making them a good choice for tea cultivation in drier regions. These soils also tend to be more stable and less prone to erosion, making them a good choice for steep slopes. However, overly heavy clay soils can be difficult to work with and may require additional amendments to improve drainage and aeration.
In addition to drainage, soil texture can also affect the chemical composition of tea leaves. Sandy soils tend to be more acidic, while clay soils tend to be more alkaline. This can affect the flavor of the tea, as well as its nutrient content. Tea plants grown in acidic soils may have higher levels of antioxidants and other beneficial compounds, while those grown in alkaline soils may have a smoother, more mellow flavor.
Soil texture also plays a role in the growth rate of tea plants. Sandy soils tend to be warmer and allow for faster root growth, while clay soils tend to be cooler and slower to warm up. This can affect the size and vigor of tea plants, as well as their susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Tea plants require a significant amount of nutrients to grow and produce high-quality tea leaves. Therefore, soil fertility is essential in tea cultivation. Fertile soil provides the necessary nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which promote healthy tea plant growth. Soil fertility can be improved by adding organic matter, such as compost, to the soil.